Mutual Fund
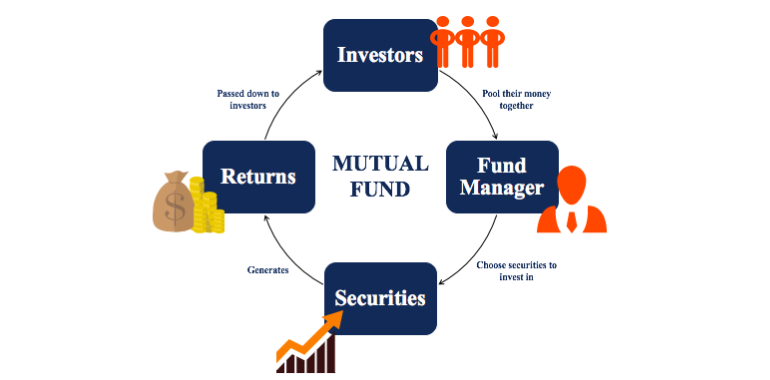
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities, managed by professional fund managers.
Equity Funds
Invest primarily in stocks, offering the potential for high returns along with higher risk
Debt Funds
Invest in fixed-income securities like bonds and government securities, providing more stable returns with lower risk compared to equity funds
Hybrid or Balanced Funds
Allocate investments across both stocks and bonds to balance risk and return
Money Market Funds
Invest in short-term, low-risk instruments like Treasury bills and commercial paper, suitable for conservative investors
The Net Asset Value represents the per-unit market value of a mutual fund scheme. It is calculated by dividing the total value of the fund's assets by the total number of units outstanding
Different mutual funds carry varying levels of risk and return potential. Equity funds are generally riskier but offer higher returns over the long term, while debt funds are less risky but provide lower potential returns
Mutual funds offer diversification by investing in a variety of securities. Diversification helps spread risk, as losses in one investment may be offset by gains in others
Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions based on market research and analysis
The expense ratio represents the total annual costs of managing a mutual fund, expressed as a percentage of the fund's assets. It includes management fees, administrative expenses, and other costs. Lower expense ratios are generally more favorable for investors
Mutual funds offer liquidity as investors can buy or sell units at the Net Asset Value (NAV) on any business day. However, liquidity can vary between different types of funds
SIP is a method of investing in mutual funds where investors contribute a fixed amount regularly (monthly or quarterly). SIP helps in rupee cost averaging and allows investors to benefit from market fluctuations
SWP allows investors to withdraw a fixed amount regularly from their mutual fund investments. It is useful for generating a regular income stream
Mutual funds are subject to capital gains tax. The holding period determines whether the gains are considered short-term or long-term, impacting the tax liability
Mutual fund investments are subject to market risks, and past performance is not indicative of future results. It's important for investors to assess their risk tolerance and investment goals before choosing a mutual fund
"Investors should carefully consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before investing in mutual funds. Consulting with a financial advisor can help in making informed investment decisions based on individual circumstances"
Let’s Get in Touch